Ultrasound Vagus Nerve Stimulation: The Emerging Non-Invasive Neuromodulation Revolution
How focused ultrasound is transforming vagus nerve stimulation from surgical procedure to painless, precision therapy
The Promise of Ultrasound VNS
For decades, vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) has required either invasive surgery to implant a device or electrical stimulation through the skin. Ultrasound VNS represents a paradigm shift—offering precise neuromodulation without breaking the skin, without implanted hardware, and without the limitations of electrical current.
Unlike transcutaneous electrical VNS, which is limited to superficial nerve branches, ultrasound can reach deep nerve structures with millimeter precision while remaining completely non-invasive.
Why Ultrasound for VNS?
Key Advantages
- Truly Non-Invasive: No surgery required—ultrasound waves penetrate tissue without incisions
- Deep Targeting: Can stimulate cervical vagus nerve trunk, not just superficial branches
- No Implanted Device: Eliminates risks of infection, battery replacement, and hardware failure
- Precision Control: Adjustable frequency, intensity, pulse duration, and focal depth
- Lower Cost: No surgical implantation ($30,000-$50,000) or maintenance costs
- Tunable Parameters: Real-time adjustment during treatment sessions
- No Medication Interactions: Purely mechanical/thermal neuromodulation
The Science of Ultrasound Neuromodulation
Ultrasound VNS works through fundamentally different mechanisms than electrical stimulation:
Primary Mechanisms of Action
- Mechanotransduction: Acoustic pressure activates mechanosensitive ion channels
- Thermal Effects: Controlled tissue heating modulates nerve conductivity
- Cavitation: Microbubble formation enhances membrane permeability
- Acoustic Radiation Force: Direct mechanical displacement of neural tissue
Types of Ultrasound VNS
Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (LIFU)
The most promising approach uses Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (intensity < 30 W/cm²) to precisely target the cervical vagus nerve without damaging tissue. LIFU can:
- Focus energy to a focal spot as small as 2-5mm
- Penetrate through skin, muscle, and vascular tissue
- Activate A-fibers and B-fibers selectively based on frequency
- Produce immediate and lasting neuromodulatory effects
Unfocused Ultrasound Applications
Broader beam applications are being explored for:
- General cervical region stimulation
- Combined with imaging for nerve localization
- Home-use devices with safety interlocks
Clinical Applications in Development
1. Treatment-Resistant Depression
Early trials show promise for patients who haven't responded to medication or traditional VNS. The non-invasive nature allows for:
- Shorter treatment protocols (weeks vs. months to assess efficacy)
- Ability to combine with other therapies
- Patient self-administration potential
2. Anxiety Disorders
Multiple studies demonstrate rapid anxiolytic effects from focused ultrasound VNS, with effects observable within single sessions.
3. Inflammatory Conditions
Ultrasound stimulation of the inflammatory reflex shows promise for:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Post-surgical inflammation
4. Epilepsy Management
As an adjunct to medication, ultrasound VNS may reduce seizure frequency without surgical implantation risks.
Technical Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Range | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 0.5 - 5 MHz | Penetration depth vs. resolution |
| Intensity | 0.1 - 30 W/cm² | Stimulation strength |
| Pulse Duration | 10 ms - 100 ms | Neural activation pattern |
| Duty Cycle | 1% - 50% | Thermal management |
| Session Duration | 2 - 30 minutes | Treatment exposure |
Safety Profile
Ultrasound VNS has demonstrated an excellent safety profile in clinical studies:
- No serious adverse events reported in clinical trials
- No tissue damage at therapeutic intensities
- No cognitive side effects unlike some medications
- No voice alteration (common with implanted VNS)
- Temporary mild effects: Occasional skin warming, mild tingling
"Low-intensity focused ultrasound represents a safe, non-invasive approach to vagus nerve stimulation with significant therapeutic potential across multiple neurological and inflammatory conditions."
The Future of Ultrasound VNS
Several developments are accelerating the field:
1. Integrated Imaging
Combining ultrasound stimulation with real-time nerve imaging allows for:
- Precision targeting verification
- Personalized treatment protocols
- Closed-loop feedback systems
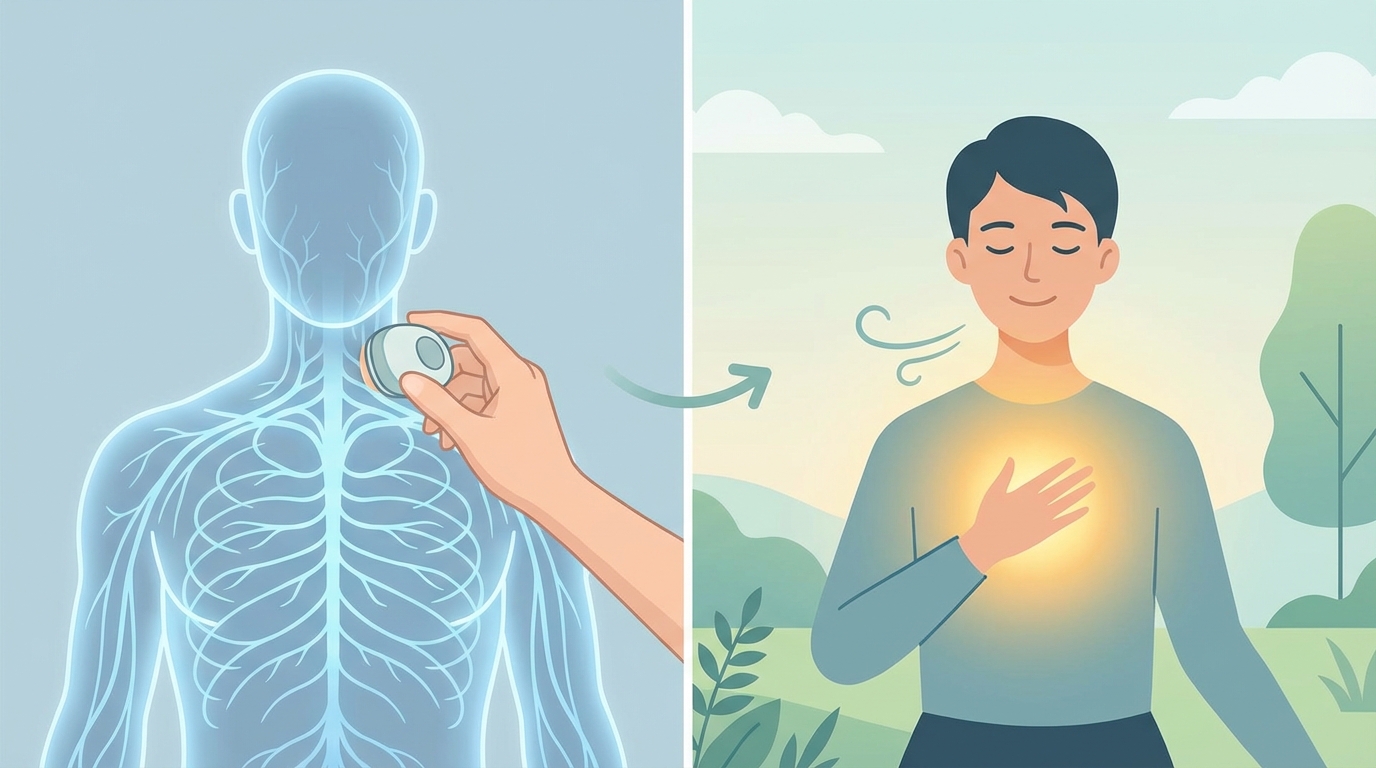
2. Portable/Home Devices
Research is advancing toward:
- Handheld ultrasound VNS devices
- Smartphone-guided home treatments
- AI-optimized stimulation protocols
3. Combination Therapies
Ultrasound VNS pairs well with:
- Biofeedback training
- Breathing exercises
- Cognitive behavioral therapy
- Cold exposure protocols
Conclusion
Ultrasound vagus nerve stimulation represents the next generation of neuromodulation—combining the proven benefits of VNS with the accessibility and safety of non-invasive treatment. While still emerging from clinical trials, the technology offers a compelling vision of precision neuromodulation without surgery.
For patients with treatment-resistant conditions, ultrasound VNS may soon provide a middle path between medication (often ineffective) and implanted VNS (invasive and expensive). The research trajectory suggests FDA approval for specific indications is likely within the next 2-4 years.